12th of March at 16h00, Carlos Baquero (FEUP) will give a presentation entitled“CRDTs: State-based approaches and efficient remote state synchronisation”
Location: G4.1
Abstract
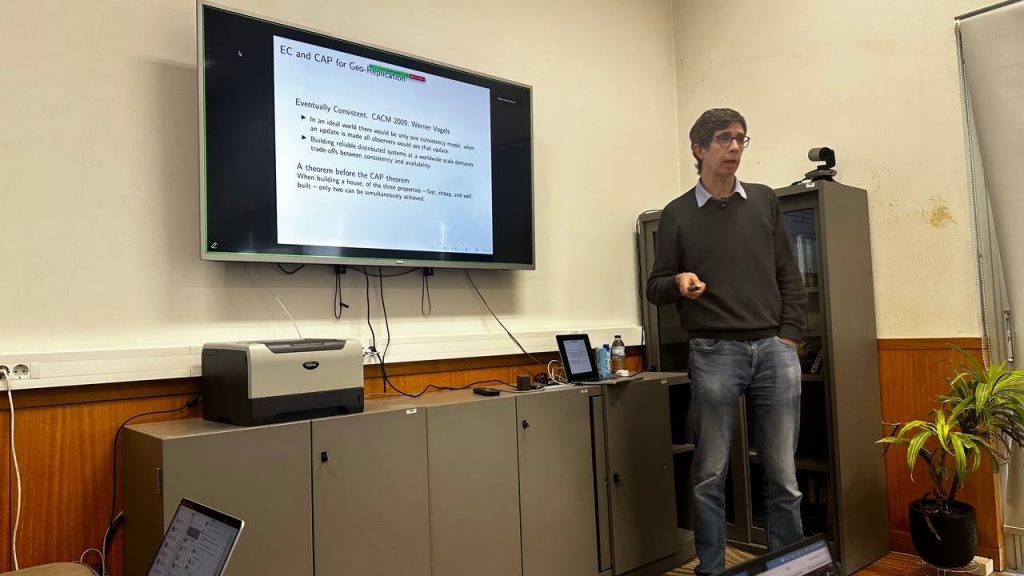
In primary-secondary replication, updating an outdated secondary replica when the primary changes is inefficient due to sizeable state and bandwidth constraints. The RSync algorithm, introduced in the nineties for file systems, solves this problem by partitioning file data, using hash functions to compare files, and transferring only the necessary data. However, RSync requires users to know which file has the most recent state and which needs updating. Like a file copy command, it has a source and a target, making synchronisation fail if either (i) here is no knowledge of which file was updated; or (ii) both files are updated.We will present ConflictSync, a solution that leverages the properties of Conflict-free Replicated Data Files (CRDTs). While RSync can handle arbitrary file data, it interprets files as byte sequences. To reconcile divergent states, we need more information on the data interpreted as a CRDT. Our solution works on any state-based CRDT and uses join decompositions, cryptographic hash functions, and Bloom filters.
Bio
Carlos Baquero is a Professor in the Department of Informatics Engineering at FEUP. Research interests cover data management in eventual consistent settings, distributed data aggregation and causality tracking. In the last years, he has collaborated with co-authors in the development of data summary mechanisms such as Scalable Bloom Filters, causality tracking for dynamic settings with Interval Tree Clocks and Dotted Version Vectors and in predictable eventual consistency with Conflict-Free Replicated Data Types. My work has been applied in several systems, including the Riak distributed database, Redis CRDBs, Akka distributed data, and Microsoft Azure Cosmos DB.